Luteinizing hormone in males – Luteinizing hormone (LH) plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system, influencing testosterone production, Leydig cell function, and spermatogenesis. Its levels and functions provide valuable insights into male health, fertility, and overall well-being.
LH is a gonadotropin hormone secreted by the pituitary gland, and its primary function in males is to stimulate testosterone production by the Leydig cells in the testes. Testosterone, in turn, is essential for the development and maintenance of male reproductive organs, secondary sexual characteristics, and overall male physiology.
LH Disorders in Males: Luteinizing Hormone In Males
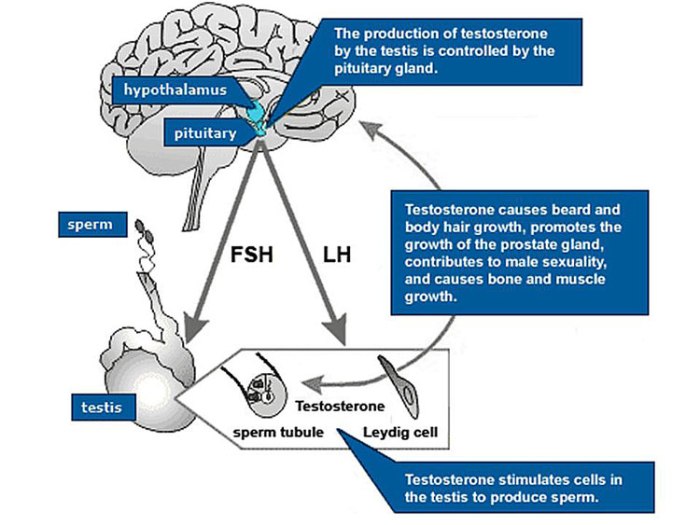
Luteinizing hormone (LH) plays a crucial role in male reproductive health. Disorders affecting LH production or function can lead to various health issues, including infertility and hypogonadism.
Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism
Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (HH) is a condition in which the pituitary gland fails to produce sufficient LH and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), resulting in impaired testicular function and low testosterone levels.
Symptoms:
- Delayed or incomplete puberty
- Reduced muscle mass and strength
- Low libido and erectile dysfunction
- Infertility
Causes:
- Genetic defects
- Tumors or other structural abnormalities in the brain
- Infections or autoimmune disorders
LH and Male Infertility
LH is essential for sperm production. Insufficient LH levels can impair spermatogenesis, leading to reduced sperm count and motility.
Symptoms:
- Infertility
- Low sperm count
- Poor sperm motility
Treatment Options for LH Disorders, Luteinizing hormone in males
Treatment for LH disorders depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
Hormone Replacement Therapy:
- Injections of LH or human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to stimulate testosterone production
Surgery:
- To remove tumors or other structural abnormalities affecting the pituitary gland
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Weight loss in obese individuals
- Exercise and stress management
LH and Male Health
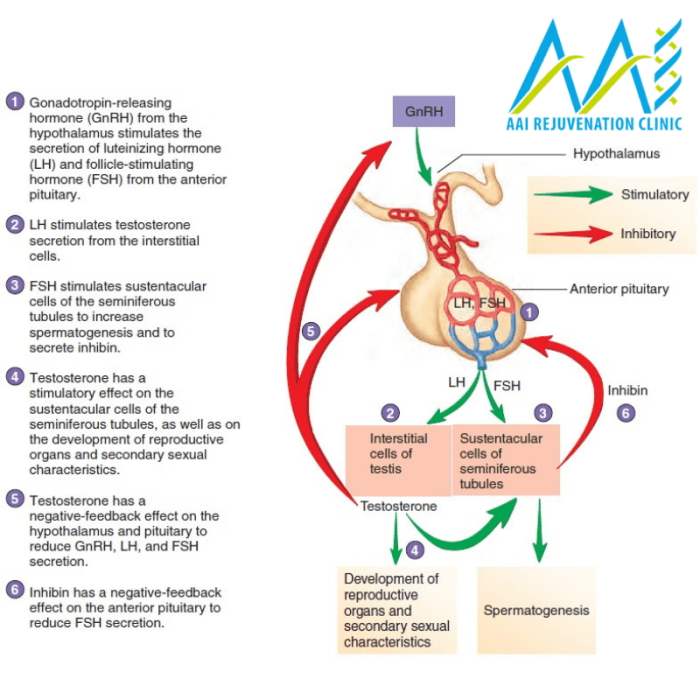
Luteinizing hormone (LH) plays a crucial role in male reproductive health and overall well-being. Understanding the relationship between LH levels and various health aspects can help in assessing and maintaining male health.
LH and Cardiovascular Health
Research suggests a correlation between LH levels and cardiovascular health in men. Elevated LH levels have been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including coronary artery disease and stroke. This association may be attributed to the effects of LH on lipid metabolism and inflammation.
LH and Prostate Cancer Development
LH has been implicated in the development of prostate cancer. Higher LH levels have been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer, particularly in men with a family history of the disease. LH may stimulate the growth of prostate cells and promote the development of prostate cancer.
LH as a Biomarker for Overall Male Health
LH levels can serve as a biomarker for overall male health. Normal LH levels indicate proper functioning of the pituitary gland and testes. Abnormal LH levels, either elevated or decreased, may indicate underlying health conditions, such as pituitary disorders, testicular disorders, or chronic diseases.
Closing Notes
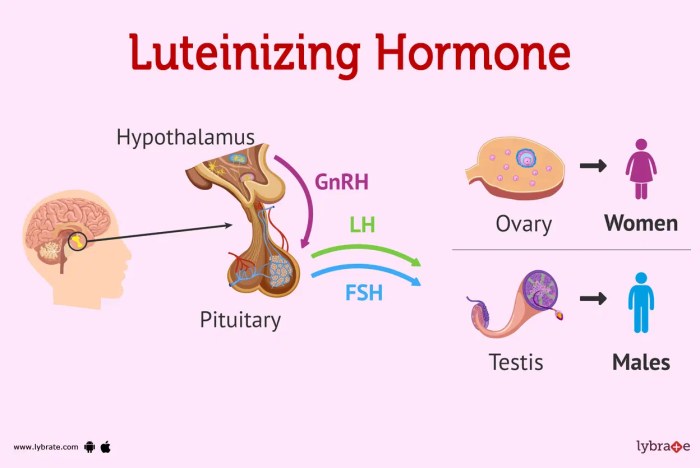
LH levels can vary depending on age, stress, medications, and other factors, and understanding these variations can aid in diagnosing and treating various health conditions. LH disorders, such as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, can affect male fertility and require appropriate medical attention.
Research continues to explore the relationship between LH and cardiovascular health, prostate cancer development, and its potential as a biomarker for overall male health. By delving into the intricacies of LH in males, we gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of male reproductive physiology and its implications for health and well-being.
FAQ Summary
What is the normal range of LH levels in males?
Normal LH levels in adult males typically range from 1.24 to 7.86 IU/L.
What factors can affect LH levels in males?
Age, stress, medications, certain medical conditions, and lifestyle factors can all influence LH levels.
What is the role of LH in male infertility?
LH is essential for testosterone production, which is crucial for sperm production and male fertility.
Can LH levels be used as a biomarker for male health?
LH levels can provide insights into overall male health, including reproductive function, cardiovascular health, and prostate health.